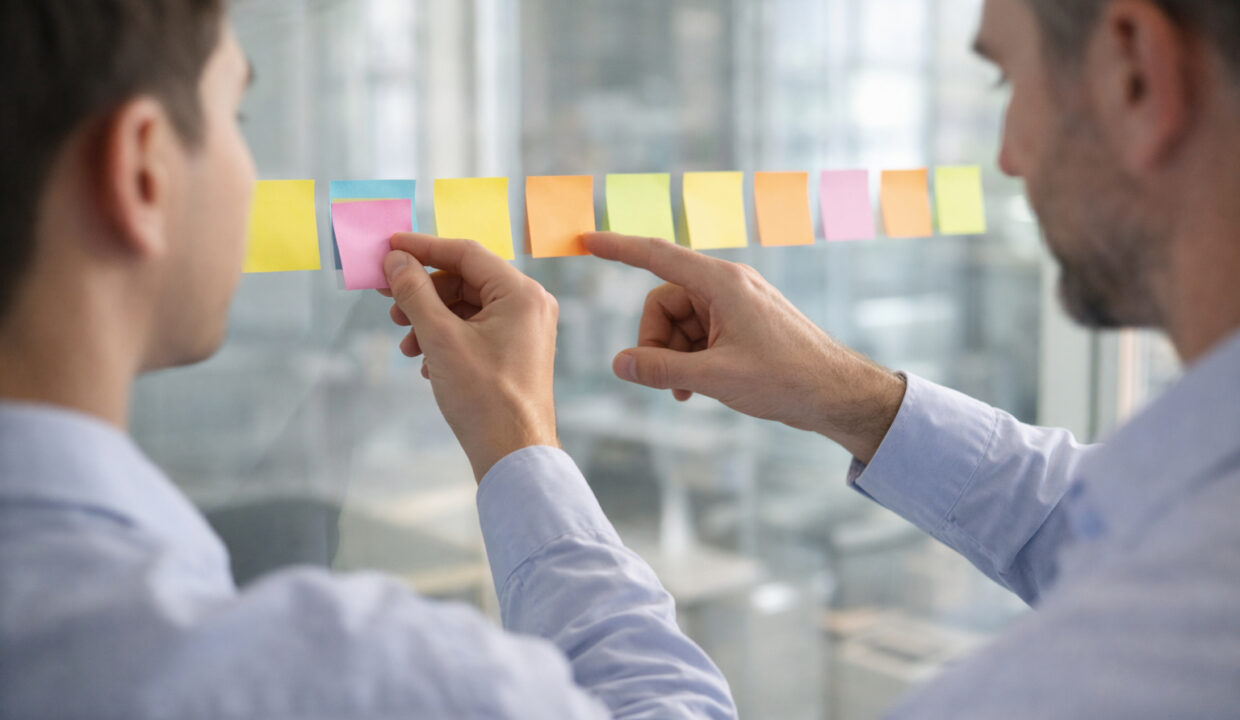
Micro-goals break larger ambitions into achievable steps that build confidence and momentum.
They reduce overwhelm by focusing attention on the next logical action rather than the entire outcome.
When used consistently, small wins compound into meaningful advancement across skills and responsibilities.
This article explains how to design, prioritize, and sustain micro-goals for steady professional progress.
Why micro-goals work
Micro-goals align effort with immediate feedback, making it easier to assess progress and adjust approaches quickly. They tap into motivation cycles by producing frequent feelings of accomplishment that support habit formation. Psychologically, this approach lowers the activation energy required to begin work and preserves willpower for higher-impact decisions. Over time, repeated completion of short tasks fosters skill improvement and credibility within teams and projects.
Adopting micro-goals does not replace long-term planning; it complements it by creating a practical path toward larger milestones. The combination of clarity and frequent reinforcement encourages consistent action without burnout.
How to create effective micro-goals
Start by identifying a clear long-term objective, then reverse-engineer the smallest meaningful step toward it. Each micro-goal should be specific, time-bound, and measurable so you can determine completion with confidence. Keep the scope limited—tasks that require under one to two hours are easier to schedule and finish, which increases follow-through. Ensure each micro-goal connects to a skill or deliverable that advances your broader priorities.
- Define the desired outcome and pick a single next action.
- Set a short deadline and a simple success metric.
- Document progress and note learned insights for iteration.
Using templates or a short checklist helps convert intentions into reliable micro-goals. Regular review sessions let you aggregate micro-wins into monthly or quarterly achievements.
Maintaining momentum and scaling impact
Consistency is essential: schedule micro-goals into your calendar and treat them as non-negotiable commitments. Celebrate completions briefly, then reflect on what worked and what needs adjustment to refine future tasks. As confidence grows, combine micro-goals to form slightly larger objectives that deliver more visible impact while preserving the habit of small, steady steps. Share progress with mentors or peers to add accountability and external perspective.
Adjust cadence when priorities shift and remove goals that no longer align with outcomes. This keeps effort focused on activities that genuinely move your career forward.
Conclusion
Micro-goals translate ambition into repeatable action that produces consistent progress.
They reduce friction, increase learning speed, and build measurable momentum over time.
Start small, review often, and scale thoughtfully to sustain professional advancement.